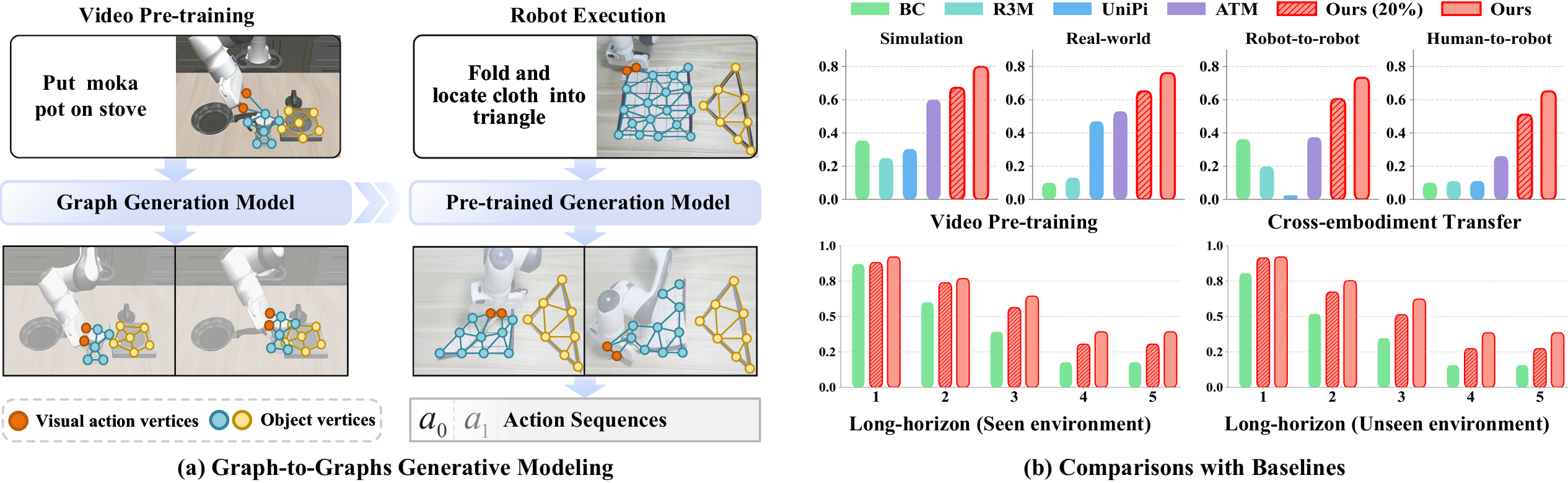
Learning from demonstration is a powerful method for robotic skill acquisition. Nevertheless, a critical limitation lies in the substantial costs associated with gathering demonstration datasets, typically action-labeled robot data, which creates a fundamental constraint in the field. Video data offer a compelling solution as an alternative rich data source, containing extensive representations of both behavioral patterns and physical principles. This study introduces G3M , an innovative framework that exploits video data via Graph-to-Graphs Generative Modeling, which pre-trains models to generate future graphs conditioned on the graph within a video frame. The proposed G3M abstracts video frame content into graph representations by identifying object nodes and visual action nodes for capturing state information. It then effectively models internal structures and spatial relationships present in these graph constructions, with the objective of predicting forthcoming graphs. The generated graphs function as conditional inputs that guide the control policy in determining robotic behaviors. This concise method effectively encodes critical spatial relationships while facilitating accurate prediction of subsequent graph sequences, thus allowing the development of resilient control policy despite constraints in action-annotated training samples. Furthermore, these transferable graph representations enable the effective extraction of manipulation skills through human videos as well as recordings from robots with varying physical configurations. The experimental results demonstrate that G3M attains superior performance using merely 20% action-labeled data relative to comparable approaches. Moreover, our method outperforms the state-of-the-art method, showing performance gains exceeding 19% in simulated environments and 23% in real-world experiments, while delivering improvements of over 35% in cross-embodiment transfer experiments and exhibiting strong performance on long-horizon tasks.